By Amanda Mintz, SPP Wetland Conservation (EVM) Program Coordinator
All photos by Ricky Osborne.
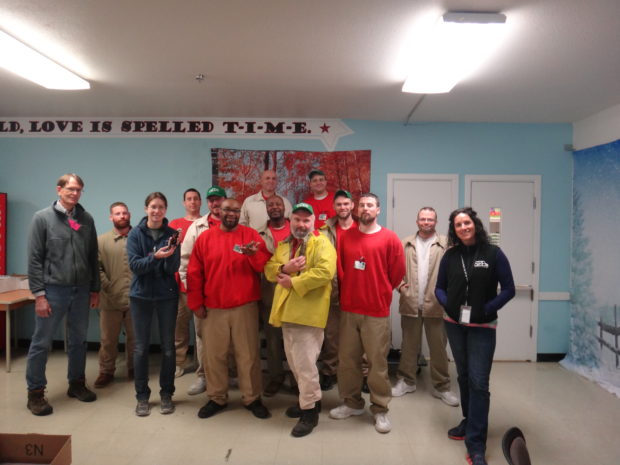
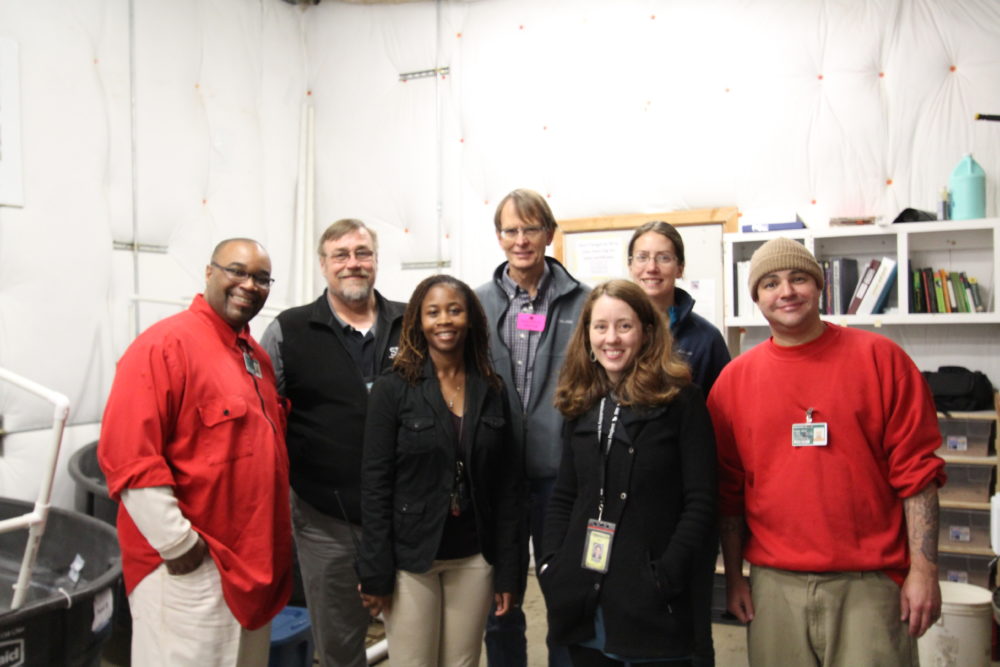
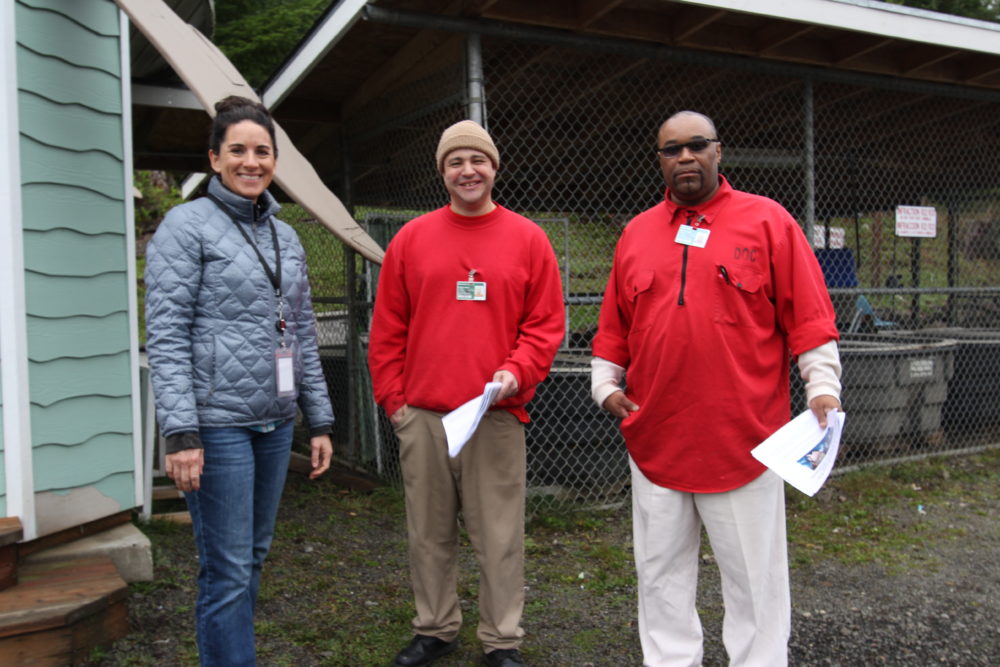
The Emergent Vegetated Mats (EVM) program at Stafford Creek Corrections Center emerged from a partnership among many stakeholders: Joint Base Lewis McChord, the Washington State Department of Fish and Wildlife, the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, the Center for Natural Lands Management, and SPP’s founding partners The Evergreen State College and Washington State Department of Corrections. On March 29th, representatives from all these organizations came together to tour the EVM nursery. We also had the chance to see other sustainability programs at work at Stafford Creek Corrections Center. Chris Idso and Kelly Peterson, DOC personnel on the leadership team at Stafford Creek, helped coordinate and facilitate the tour, and we were joined by our project liaisons Mike Granato and Ed Baldwin. It was the first visit to both the EVM nursery and a prison facility for many of our partners.

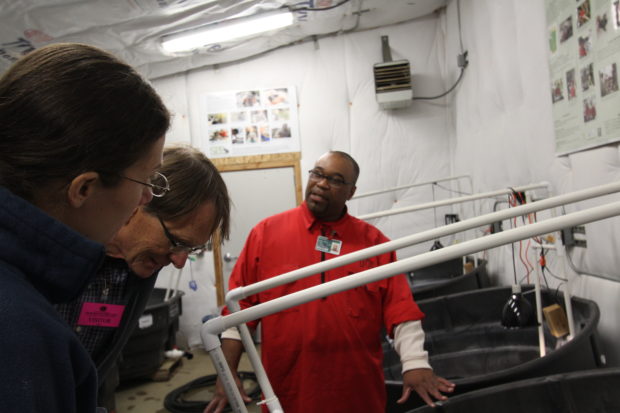
Partners view the systems inside the EVM greenhouse. Photo by Ricky Osborne.
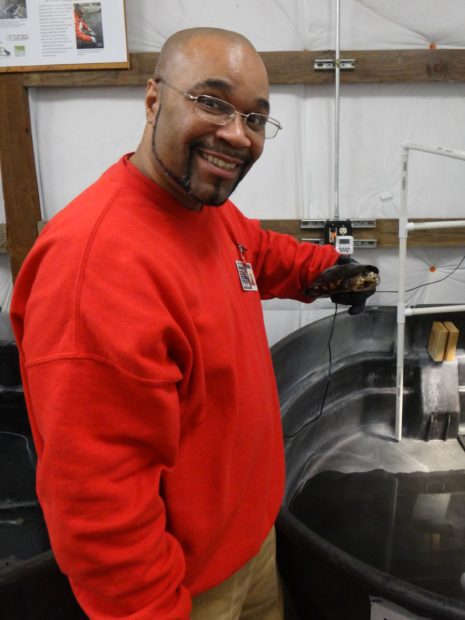
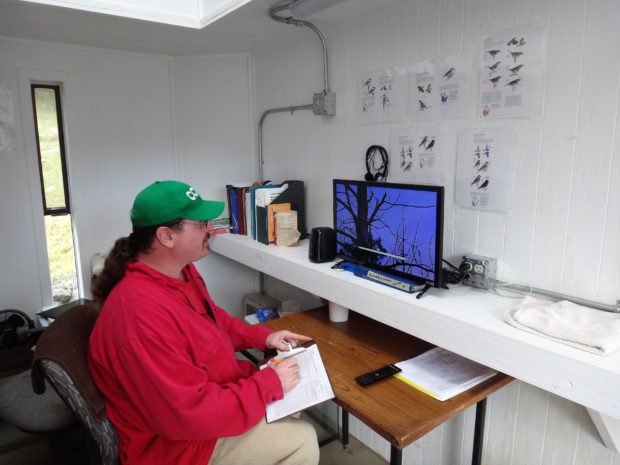
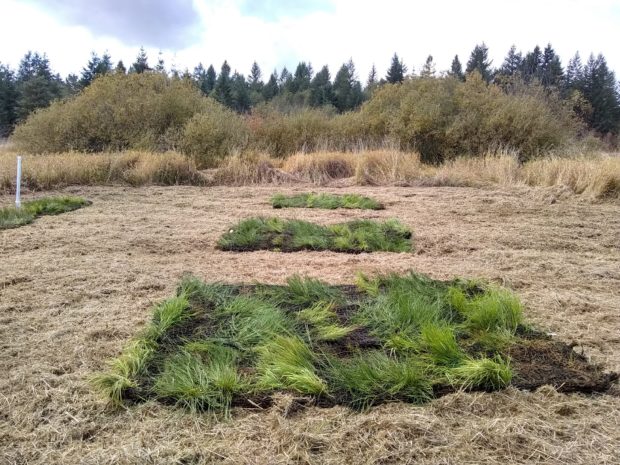
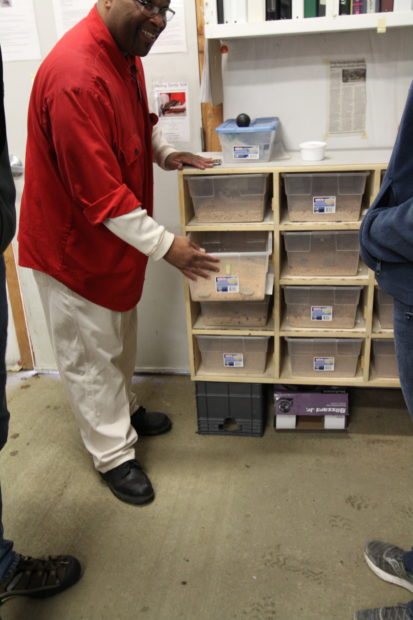
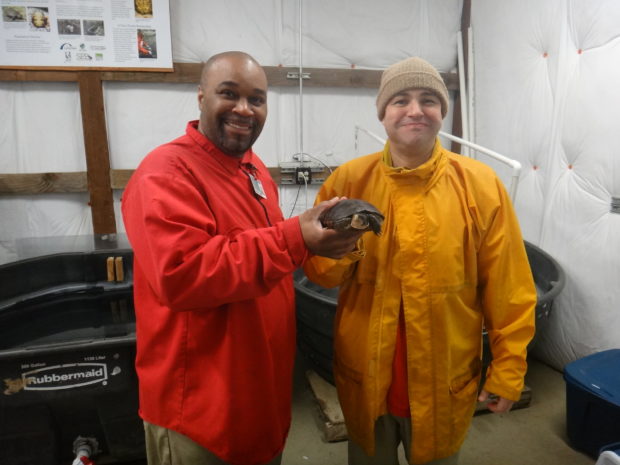
We started in the EVM greenhouse, where we discussed past mat production and future production potential. Last year, we produced and installed more than 100 mats at south Puget Sound restoration sites! The technicians described how the system works, and we all stopped to marvel at the fish—about 130 koi provide most of the nutrients absorbed by the wetland mats.

Not just beautiful, koi are hardy fish adaptable to unexpected changes in water chemistry; this makes them perfect for an aquaponics system. Photo by Ricky Osborne.
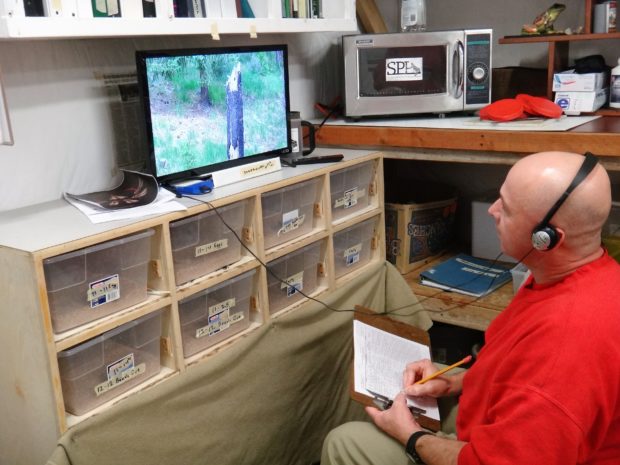
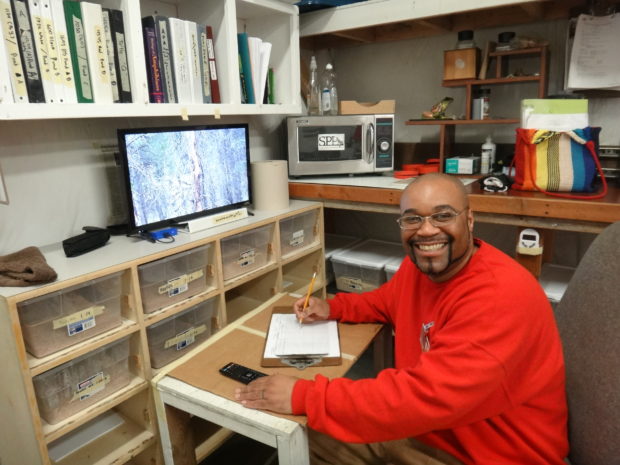
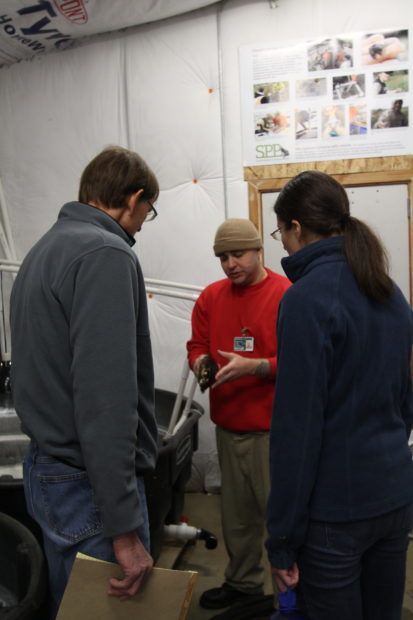
Technician Brian Bedilion, who has worked for the EVM program since its inception in 2016, explained how working for SPP has impacted his self-confidence and goals for his future. His creativity and ability to troubleshoot on-the-fly have been integral to the success of the EVM program. Brian went home on April 13; we wish him the best, and hope to see him in the field!

Technician Brian Bedilion shares how the EVM program has influenced his life. Photo by Ricky Osborne.

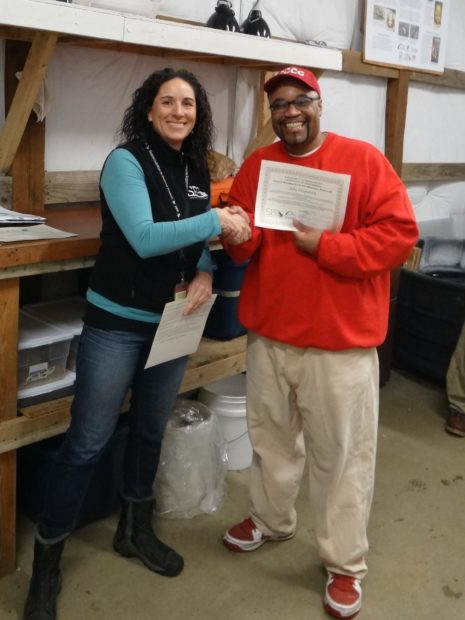
SPP EVM Coordinator Amanda Mintz and Brian Bedilion say farewell at the end of the EMV portion of the tour. Photo by Ricky Osborne.
After touring the EVM greenhouse, we went inside the fence to see the prairie conservation nursery, gardens, and other sustainability programs hosted by Stafford Creek. Every living area has dedicated garden space for its residents. A larger space outside the education building is intended for men serving life sentences, and is known as the Lifer Garden. The Lifer Garden and one other at Stafford Creek grow produce for local food banks. Last year, incarcerated individuals at the prison grew and donated almost 12,000 pounds of produce!

With help from Grounds Maintenance Supervisor and SPP Conservation Nursery Liaison Ed Baldwin, the Lifer Garden is designed, built and maintained by individuals serving life sentences. Photo by Ricky Osborne.

Ed Baldwin and a technician talk outside the Prairie Conservation Nursery greenhouses. Photo by Ricky Osborne.

The prison’s grounds crew produces plants for the prison gardens, and also cultivates plants for SPP’s Prairie Conservation Nursery. Here, a technician demonstrates propagation by cutting. Photo by Ricky Osborne.

Chris Idso, left, is the longest-term champion of sustainability programs at Stafford Creek, and he’s got a good sense of humor. Photo by Ricky Osborne.
The tour ended with visits to the shop areas, where partners saw bicycle and wheelchair repair. Like all the other programs we saw at Stafford Creek, these programs bring together partners to create something of value for the benefit of our environment and our communities.