Text by Jessica Brown, SPP Turtle Program Coordinator, Philip Fischer, U.S. Forest Service volunteer and Adam Mlady, Biological Science Technician.
Photos by Jessica Brown

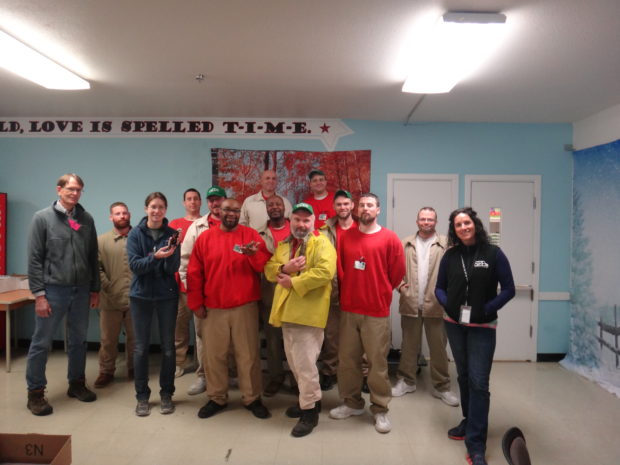
Biological Science Technician Adam Mlady holding two of the Western Pond Turtles currently housed at Cedar Creek Correctional Center.
Cedar Creek Corrections Center (Cedar Creek) was home to the very first endangered animal program in a prison: they raised and released hundreds of Oregon spotted frogs from 2009-2015. In 2018, ecological conservation at Cedar Creek is thriving and evolving to encompass a small array of conservation and sustainability programs. Offering an array of programs allows us to partner with a larger group of incarcerated technicians; there are five at this time, and we plan to add a few more. All participants will have a new position title of Biological Science Technicians, and will receive education and training in the turtle, beekeeping and woodpecker programs, and—later on—a new aquaponics program.
Turtles
Cedar Creek hosts endangered pond turtles that need daily attention; from Technician Adam Mlady’s writing last month, “currently we have two females, one male, and are expecting seven more to be dropped off later today…Taking care of them is very rewarding. I get a sense of unity and accomplishment in ensuring they are clean and fed, and working them back to health. It’s even a sustainable project to feed them! They eat a mix of goodies, but one of the days the pond turtles get mealworms, which we grow and harvest ourselves. Eggs to larva to pupae to beetle, we are hands-on (gloved of course!) the whole way through.”
Woodpeckers

USFS trainers, SPP coordinator, and participants of the woodpecker nest monitoring project training pose with bird specimens.
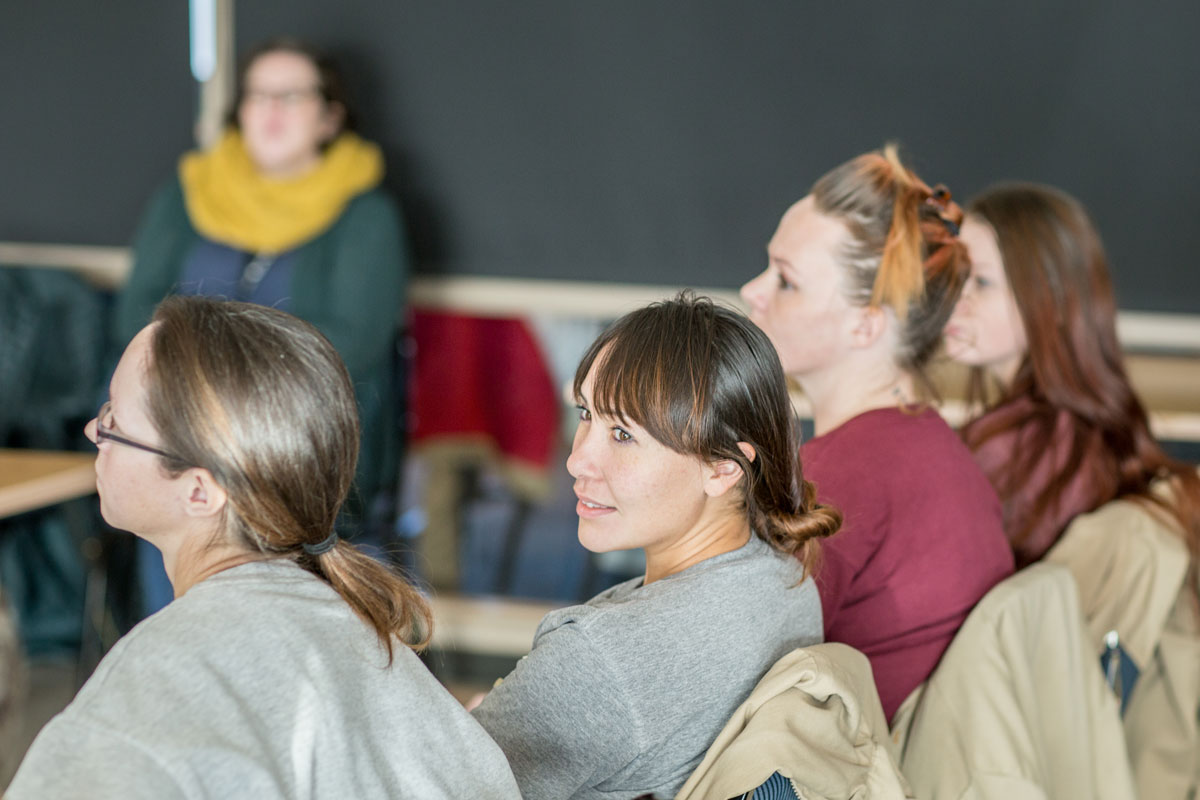
In November, the Woodpecker Nest Monitoring Project was launched with a two-day training for all five turtle technicians, four greenhouse workers, and two other interested individuals. The purpose of the Woodpecker Nest Monitoring Video Review is to support a multi-year research project through the U.S. Forest Service (USFS) focused on identification of nest predators.
Woodpeckers are a keystone species that provide cavities not only for their own nesting use, but also for a broad spectrum of secondary cavity users including small mammals and other birds. Video footage comes from cameras operating 24/7 at cavity nests. This is the only sure way to document nest depredation, however, reviewing the enormous amount of video footage requires an equally enormous amount of reviewer time. In order to accurately monitor video footage, correctly identify species, and describe animal behaviors, reviewers need considerable training.
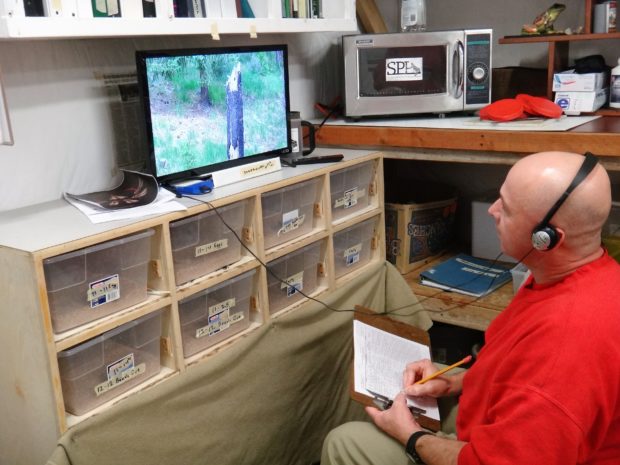

Biological Science Technician Modesto Silva reviewing video footage of a Northern Flicker cavity nest. This video station sits atop the mealworm rearing bins for the western pond turtle program.
Participants at Cedar Creek received six hours of education and training from Teresa Lorenz, USFS biologist and Phil Fischer, USFS volunteer, covering woodpecker, raptor, song bird, and small mammal identification; background information relating to the project, including project protocol and species behavior descriptions; and monitoring and data recording techniques. In the past, video monitoring has only been performed by undergraduate students, however, collaboration between USFS and SPP has made it possible to also bring this type of education and experience into prison.
And coming soon…
Cedar Creek has long had a productive greenhouse, including a small aquaponics system. The old aquaponics will be replaced with a more productive system designed by Symbiotic Cycles LLC, an Olympia-based company dedicated to the application of regenerative food production through aquaponics. The new design will support production of fresh greens year round for use in the kitchen.
Technician Mlady has said, “I’m really excited about the upcoming aquaponics pond we will be building. It is huge, and tucked away safely up in our camp’s greenhouse. Once we get the plumbing correctly set up, the koi fish will be able to fertilize our selected plants and vegetables. Brilliant system.” Aquaponics training will start sometime this March, and the system should be up and running soon after.
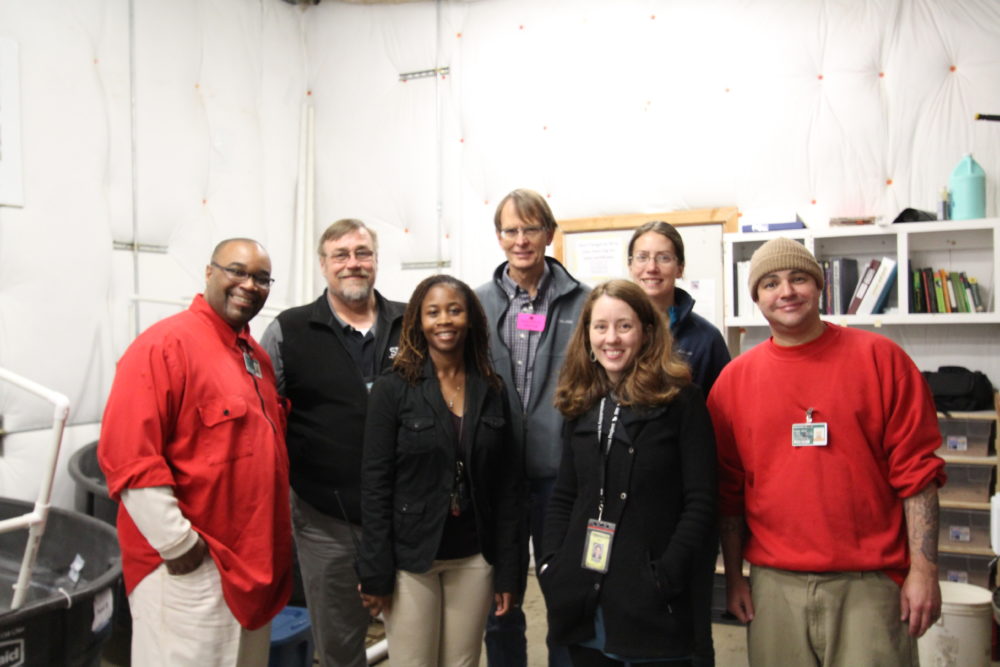

Partners in endangered species conservation for Cedar Creek Corrections Center, from left to right: Technician, John Fitzpatrick, Superintendent Douglas Cole, Loretta Adams (SPP Liaison), Philip Fischer (U.S. Forest Service), Kelli Bush (SPP Co-Director, Teresa Lorenz (U.S. Forest Service), Technician William Anglemyer). Photo by Jessica Brown.